(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) rise (b)(*) drop (c) stay the same
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
- matter.
- energy.
- the absolute truths about the natural world.
- (*) the general principles underlying natural phenomena.
- the application of science to the needs of human beings.
- the backward part of the planet's epicycle on its orbit around Earth.
- (*) a result of Earth's motion: as Earth passes another planet, that planet appears to move backward as seen against the background stars.
- due to the oscillatory back-and-forth motion of planets on their circular orbits around Earth.
- due to the irregular motion of the celestial sphere carrying the background stars.
- due to slowing down and speeding up of the Earth on its orbit around the sun.
- the use of mathematics;
- the use of quantitative measurements;
- the use of only those theories which are known to be true;
- the usefulness of its results for human well-being and technological progress;
- (*) the possibility of testing its predictions by experiment or observation, whereby they can be disproved (falsified);
- (*) circles-within-circles (epicycles on deferents) around Earth.
- circles around the sun.
- circles around Earth.
- circles-within-circles (epicycles on deferents) around the sun.
- elliptical orbits around the sun.
- (*) The sun is just one of a large number of stars, located in the fringes of the Milky Way galaxy, which itself is just one of many galaxies.
- The sun is at the center of the universe.
- Earth is at the center of the universe, and the sun orbits around the earth.
- The sun is just one of the many stars clustered near the center of the universe.
- The sun is a one-of-a-kind and isolated star that is far outside of all the galaxies in the universe.
- a single tiny object without any internal structure, not made of parts.
- made of positively charged matter balls with electrons embedded in it.
- made of a cloud of protons and electrons.
- made of protons, electrons and ions.
- (*) made of a small, massive positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons which are rather far from the nucleus.
- they don't really exist - they are just a convenient model of matter.
- they are so tightly packed that one cannot separate them from the other atoms.
- they are much smaller then the aperture (opening) of any microscope.
- (*) the wavelength of visible light is too long compared to the size of atoms.
- the wavelength of visible light is too short compared to the size of atoms.
- both reactions create oxygen;
- (*) both reactions involve oxidation and liberate energy;
- both reactions consume energy;
- both reactions use energy to convert carbon dioxide into hydrocarbon componds;
- there is no similarity - they are completely different processes;
- 5
- 20
- (*) 100
- 1000
- too many to count.
- 3
- 4
- (*) 24
- 48
- cannot be determined from the information provided.
- 4000 km
- 6500 km
- 13000 km
- (*) 40000 km
- 65000 km
-
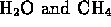
- ammonia and water
- methanol and
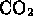
- (*) water and carbon dioxide
- hydrogen and oxygen
- (*) lead to an increase in volume due to the higher speed of the molecules.
- increase the density, because of the higher pressure.
- decrease the pressure since hot air is thinner (less dense).
- increase the pressure since heat equals pressure.
- not have any influence on the density of the air.
- 109 times
- 1090 times
- 12000 times
- 157000 times
- (*) 1.3 million times
-
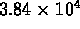
-
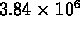
- (*)
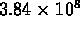
-
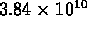
-
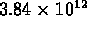
-
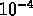 meters
meters
-
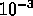 meters
meters
- (*)
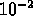 meters
meters
- 0.5 inches
- 2.54 inches
- water molecule
- oxygen atom
- hydrogen atom
- electron
- (*) alcohol molecule
- (*) are in the same column (``group'') of the periodic table.
- are in the same row of the periodic table.
- have a similar number of electrons.
- have about the same weight.
- have a nucleus of about the same size.