(a)(*) True (b) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a) True (b)(*) False
(a) True (b(*) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
(a)(*) True (b) False
- You try to lift a tree blocking your driveway, but it doesn't budge.
- (*) Your brother throws his dirty clothes into the corner of his room.
- Your mother holds a sleeping baby.
- You work hard studying for your physics exam.
- You spend many hours standing in line for a ticket to the football game.
- 0 J
- 5 J
- (*) 10 J
- 15 J
- 20 J
- (*) kinetic
- gravitational potential
- elastic
- thermal
- chemical
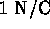
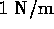
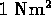
- (*)
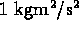
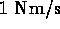
- chemical energy
 gravitational potential energy
gravitational potential energy
- thermal energy
 chemical energy
chemical energy
- kinetic energy
 chemical energy
chemical energy
- (*) chemical energy
 thermal energy
thermal energy
- chemical energy
 kinetic energy
kinetic energy
- 10 Joules
- 10 watt-hours
- 10 kilowatts
- 10000 Joules
- (*) 10 kilowatt-hours
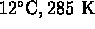
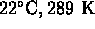
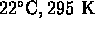
- (*)
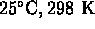
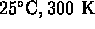
- The calorie unit used to measure heat and the Calorie unit used on food labels are exactly the same unit.
- The larger the temperature difference between two objects, the more slowly will heat be transferred from one to the other.
- The main reason we wear clothes is in order to reduce heat loss by radiation.
- A gallon of boiling water and a pint of boiling water contain the same amount of thermal energy.
- (*) A gallon of boiling water and a pint of boiling water are at the same temperature.
- 11%
- (*) 20%
- 35%
- 80%
- 120%
- 16%
- 37%
- (*) 56%
- 89%
- cannot be determined from the information provided.
- 3 J
- 30 J
- (*) 60 J
- 300 J
- 600 J
- (*) is 1/4 its previous value;
- is halved;
- is doubled;
- is 4 times its previous value;
- stays the same;
- 3.3 cm
- 33 cm
- (*) 3.3 m
- 8.9 m
- 328 m
- (*) zero amplitude;
- twice the wavelength and the same amplitude as each of the individual waves;
- twice the wavelength and twice the amplitude;
- the same wavelength and the same amplitude;
- the same wavelength and twice the amplitude;
- blue light;
- (*) radio waves;
- infrared light;
- X-rays;
- red light;
- In an electromagnetic wave, the magnetic field is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
- The speed of propagation of electromagnetic waves can be calculated from Maxwell's equations.
- Electromagnetic waves can be generated by accelerated charges.
- (*) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal waves, i.e. the disturbance in the electric field is in the direction of wave propagation.
- Electromagnetic waves do not need a material carrier medium to travel in -- they can exist in vacuum.
- newton
- volt
- ohm
- coulomb
- (*) ampere
- 0 A
- 0.5 A
- (*) 1 A
- 2 A
- 4 A
- (*) An electric current flowing in a copper wire consists of protons moving along the wire from the high potential to the low potential end of the wire.
- Electric motors are based on the facts that electric currents generate magnetic fields, and that magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges.
- When a wire loop is moved in a magnetic field, an electric field is created which causes a potential drop along the wire. This phenomenon is used in the generation of electric energy.
- Magnetic fields which vary in time cause the creation of electric fields.
- The force exerted by a magnetic field on a moving charge is stronger the faster the charge moves.
- In order to define position, velocities, accelerations,..., one has to define frames of reference with respect to which these quantities are measured.
- In an inertial frame, the law of inertia is valid.
- Any frame moving in uniform motion with respect to an inertial frame is also an inertial frame.
- (*) According to Galilean relativity, all inertial frames of reference are equivalent for all laws of physics.
- Velocities depend on the frame of reference, but accelerations are the same in all inertial frames.
- measured the speed of the ether wind to be equal to the speed of light.
- (*) measured the speed of light in different directions with respect to the Earth's motion to be the same, thus providing evidence against the existence of the ether as the medium for the propagation of light.
- found that the speed of light was different in different directions, in contradiction with Maxwell's equations.
- was not sensitive enough to be able to measure the influence of the ether wind on the speed of light.
- used very precise clocks to determine differences in traveltime of light rays split by semi-transparent mirrors.
The special theory of relativity
- solved the inconsistency between mechanics and electrodynamics with respect to Galilei invariance.
- states that all inertial frames are equivalent for all laws of physics.
- states that the speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, independently of their relative state of motion.
- does away with Newton's concept of absolute space and time, replacing it by a 4-dimensional space-time continuum.
- (*) provides a new explanation of gravity in terms of the geometry of space.