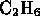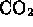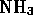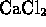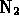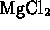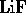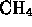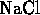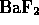PHYSICS 1020 - Spring 1997
SOLUTION TO FOURTH EXAM
31 March 1997
(Correct solution is indicated by ``(*)'')
- The speed of electromagnetic waves calculated from Maxwell's equations
is the same as the speed of light in vacuum.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The speed of light depends on the relative motion of reference frame,
source, medium, and observer.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The observed frequency of light is always the same as that
of the light emitted by the source, independently of the relative motion of light
source and observer.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Any system (frame) moving with uniform velocity relative to
an inertial frame is also an inertial frame.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Kristin claims that, by precise measurements performed entirely inside
her laboratory, she has determined that the absolute speed of her laboratory is 28 km/s.
Do you think she is right?
(a) Yes (b)(*) No
- In the SI system of units, the meter is defined in terms of the speed of light.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- By measuring the speed of light in different directions with respect to the direction of
motions of the Earth, Michelson and Morely provided evidence for the effects due to
``ether wind", thus proving the existence of the ether as the medium in which light propagates.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Your friend Jane is moving past you at high speed. She thinks that your clock
goes much slower than hers, but she is wrong. In reality, since she is moving, it is
Jane's clock which goes slower than yours.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Apart from small deviations dictated by allowed air-corridors, airplanes travel along
great circles because these are the geodesic lines
on the
surface of the earth.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- When light travels close to a massive object, its path is bent due to
gravity. This effect was first observed during a solar eclipse in 1919.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The principle of the constancy of the speed of light applies only to
visible light; since they have a different frequency, the speed of UV-light and
microwaves can be different depending
on the motion of the source.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Two events, remote from each other, which are observed to happen simultaneously
by one observer are
in general observed to occur at different times by another observer who is in motion
relative to the first one.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- If the speed of light were infinite, all observers would agree on the
simultaneity of two events, even for events happening at different locations.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The redshift observed in the light coming to us from distant galaxies is
evidence for the expansion of the universe.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- When a very massive star has used up all its fuel,
the gravitational force is no longer balanced by radiation pressure;
the ensuing gravitational collapse of the star can lead to the formation
of a black hole.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- All phenomena involving light can be explained by its wave nature.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- In some aspects, electrons behave like waves.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Standing waves on a string are generated by the superposition
of two waves travelling in opposite directions.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The spectrum of thermal radiation emitted by a black body can be
predicted correctly (i.e. in agreement with experiment) by using Maxwell's
equations and classical thermodynamics.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The photoelectric effect can be explained by assuming that light is
not a continuous stream of electromagnetic radiation, but rather consists
of wave
packets of finite length and well-defined energy (photons).
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The ``Big Bang" is the loud noise due to the explosion of a nuclear bomb.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Ice cubes are so efficient in cooling your drink because of water's big
latent heat of fusion (i.e. it requires a lot of energy to melt ice).
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Water is a liquid at ``normal'' temperatures because of the polar nature of
its molecules which makes them stick together.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Noble gases like argon and krypton are chemically very active and form many
compounds.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Halogens like chlorine and fluorine are nearly inert and do not react
readily with other elements.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The orbital angular momentum of an electron in an atom can have any
value.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The electron is a member of the class of particles called ``fermions.''
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Some atoms are particularly stable because all electrons are in the same
low energy state.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The two electrons in the ground state of the He atom have their spins
parallel to each other.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The noble gas configuration is a particularly stable arrangement of
electrons in an atom.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- In a metallic bond, the valence electrons are tightly bound to particular
atoms and cannot move.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Which of the following two elements is more electronegative, i.e. has
a stronger ability to attract electrons?
(a) Boron (B) (b)(*) Fluorine (F)
- A single atom can absorb light of any wavelength.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- When two waves are in phase, they can reinforce each other by
constructive interference.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Sound waves travel faster in interplanetary space than in the Earth's
atmosphere.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- The amplitude of the standing wave on a string will be maximal when
the frequency of the exciting disturbance (e.g., wiggling) is equal to
one of the string's characteristic frequencies.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- (Photoelectric effect:) The kinetic energy of the electrons emitted
from the surface of a photosensitive metal grows with the frequency of
the incident light.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The electric charge of an electron is equal and opposite to that of a
proton.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- When we observe that the spectral lines in light from a distant star are
shifted towards shorter wavelengths, we conclude that the star is receding from
us.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Elements in the same column (same group) of the Periodic Table
have similar properties.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing
size of the atom.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Electromagnetic waves need a material medium for their propagation.
(a) True (b)(*) False
- Diffraction gratings are used to measure the wavelength of light.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- When an atom de-excites, i.e. an electron jumps from a higher
energy state to a lower state, light is emitted whose wavelength is determined
by the energy difference between the two states.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- The set of wavelengths emitted by an atom or molecule is distinctive and
can be used to identify it.
(a)(*) True (b) False
- Sissy and Sassy are twins. Sissy goes on a trip at close to the speed of light
and then returns to Earth.
- Since they both experience the same laws of physics, they must have the same
age when they meet again on Earth.
- Earth is a special frame of reference in which clocks go faster, and so Sissy stays younger than Sassy.
- They both have still the same age, but they are much younger than they would be if
Sissy had not gone on her trip.
- Since neither of them is a preferred observer, they must come to equivalent
conclusions about each other:
according to Sissy, Sassy is now much older than she is, while according to Sassy, Sissy is
now older than Sassy.
- (*) Since Sissy spent part of her trip in an accelerated frame of reference, the
reference frames of the two
are not equivalent; due to time dilation effects, Sissy is now much younger than Sassy who
stayed behind.
- Which of the following compounds is formed by an ionic bond?
-
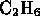
-
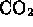
-
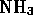
- (*)
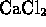
-
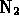
- Which of the following is a molecule formed by a covalent bond?
-
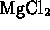
-
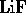
- (*)
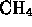
-
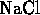
-
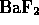
- In ``everyday life'' we do not notice evidence for the wave nature of
objects that we deal with because
- the speed of the particle waves is so large that we cannot see them;
- (*) the wavelength associated with everyday objects is so much smaller than
their size that the wave effects play no important role;
- the wavelength associated with everyday objects is so much larger than
their size that the wave effects play no important role;
- only small particles in atoms have wave properties;
- these wave aspects would only become apparent in UV light which we cannot
see.
home page for phy1020
Fri Apr 4 11:27:14 EST 1997