SPEED OF LIGHT
- speed of light in vacuum
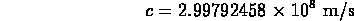
note that this is a precise equality since meter is defined by this equation (since 1983)
- measurements:
- first attempt by Galilei: measure time for light to travel to distant mountain and back; unsuccessful since time measurement not precise enough.
- Ole (Olaus) Römer (1675):
moons of Jupiter appear later when Earth farther away from Jupiter - Hippolyte Louis Fizeau (1849):
with rotating cogwheel and semitransparent mirror;
light reflected off semitransparent mirror passes between cogs of cogwheel; light reflected off distant mirror, passes again between cogs;
determine speed of light from revolution frequency of cogwheel for which light passes or is blocked; - Léon Foucault (1859):
with semitransparent mirror and rotating mirror
speed of light in water smaller than in air; - Albert Michelson, Edward Morley (1887):
used interferometer to measure traveltime differences
measured speed of light in different directions with respect to direction of Earth's motion;
found that speed of light same in all directions -- independent of motion of source and receiver (``no ether wind'').
REFERENCE FRAMES, RELATIVITY
- frame of reference = physical surroundings
- from which observer observes and measures,
- with respect to which physical quantities are defined
(e.g. positions, velocities, accelerations..)
- = e.g. a place on the surface of the Earth, an airplane, a train, ...
- description in different reference frames:
- ``event'' = something well-defined happening at well-defined place at well-defined time;
- events described by coordinates defined relative to frame of reference;
- coordinates = specification of place and time
- ``transformation'' = changing from description in one frame to another frame;
- transformation equations relate coordinates in different frames to each other;
- `` Galilei invariance'':
Newton's Laws found to give consistent description of motions in frames at rest with respect to the surface of the Earth;
but also in frames of reference which are in uniform motion with respect to surface of Earth.- inertial frame (inertial system):
= frame of reference in which law of inertia holds- any system (frame) moving with uniform velocity relative to an inertial frame is also an inertial frame;
- ``Galilei transformation''
- = changing from one inertial frame to another frame;
- = set of equations relating quantities measured in one inertial frame to those measured in another inertial frame;
- position is affected by transformation:
e.g. position in one frame changes even if object of event at rest with respect to other frame; - ``addition of velocities'':
velocity with respect to one frame = (velocity in other frame) plus (velocity of other frame); - time is the same in both frames;
- accelerations, forces are same in both frames.
- ``Newtonian principle of relativity'':
- the laws of mechanics are the same in all inertial frames (they are ``invariant under Galilei transformation'');
- there is no mechanics experiment or mechanical measurement that allows us to determine whether our frame of reference (our laboratory) is ``at rest'' or in ``uniform motion'';
- there is no mechanical measurement performed entirely inside our laboratory that allows us to determine its ``absolute velocity''.
CRISIS OF NEWTONIAN PHYSICS
- At end of 19th century, physicists realized disparity between two best established fields of physics: between Newtonian mechanics (Newton's laws) and electrodynamics (Maxwell's equations)
- Newton's laws
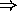 measured velocity of moving body depends on velocity of observer
measured velocity of moving body depends on velocity of observer
- Maxwell's equations contain parameters which define speed of light, apparently independent of observer;
- Newtonian (Galilean) principle of relativity:
(follows from Newton's first law, the law of inertia)
laws of mechanics must be the same for a fixed observer as for an observer in uniform motion with respect to the first observer;
neither of the two observers can tell by an experiment which of them is ``really'' moving and which of them is ``really'' at rest. - note restrictions in this principle of relativity:
- only for mechanics (deals with massive bodies - not with light waves);
- uniform motion (i.e. no acceleration).
- Einstein's theory of relativity eliminates these restrictions:
- special theory of relativity: generalize beyond mechanics, include light;
leads to new concept of time and space - ``space-time''; - general theory of relativity: generalize beyond uniform motion, allow acceleration;
leads to new concept of space-time and gravitation.
- special theory of relativity: generalize beyond mechanics, include light;
SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY
A. Einstein: ``Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper'' (1905) (on the electrodynamics
of moving bodies):
Two postulates:
- (I)
- Principle of Relativity:
The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames, i.e. all inertial frames are equivalent. - (II)
- Principle of the Constancy of the speed of light:
The speed of light in free space (vacuum) is always constant = c, independent of the relative motion of the inertial frames, the source, and the observer.
Notes:
- ``inertial frame'' means frame of reference moving with uniform velocity (i.e. not accelerated, in straight line);
- note ``laws of physics'', not just mechanics
- Newton:
there is absolute space in which all motions can be compared;
and ``absolute, true and mathematical time, of itself, and from its own nature flowing equably without relation to anything external...'' - theory of relativity relates measurements of distance -space - and measurements
of time intervals - time - to speed of light
i.e. the two absolutes of Newtonian physics - space and time - replaced by one absolute - speed of light
Main consequences of special relativity:
- time dilation - ``proper time''
- length contraction - ``proper length''
- relativity of simultaneity
- relativistic mass increase, ``rest mass''
- mass-energy equivalence
- interrelationship between spatial distances and time intervals
 four-dimensional ``space-time''
four-dimensional ``space-time''
- speed of light is limiting speed
- new rule for addition of velocities
- relativistic Doppler effect
- simplification of description of magnetic forces
TRANSFORMATIONS BETWEEN REFERENCE FRAMES
``GALILEI TRANSFORMATION''
- = set of equations relating quantities measured in one inertial frame to those measured in another inertial frame;
- consider two inertial frames S, S', where frame S' moves with respect to frame S with constant velocity v in the positive x direction;
- coordinates of some event are
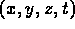 in frame S,
in frame S,
and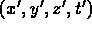 in frame S'
in frame S'
- relation between the two:
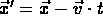

- velocities in the two frames:
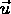 in frame S,
in frame S, 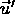 in frame S'
in frame S'
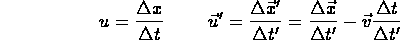
now since
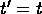

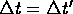 , it follows that
, it follows that 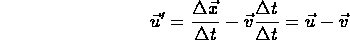
- ``addition of velocities'':
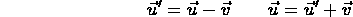
i.e. velocity (
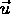 ) in first frame (S) = velocity (
) in first frame (S) = velocity ( 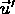 ) in second frame (S' ) plus velocity (
) in second frame (S' ) plus velocity ( 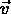 ) of second frame (S' ) with respect to first frame (S);
) of second frame (S' ) with respect to first frame (S); - acceleration:
S, S' inertial frames, i.e.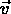 is constant (uniform motion!)
is constant (uniform motion!)
therefore accelerations are the same in both frames
LORENTZ TRANSFORMATION
- consider two inertial frames S, S', where frame S' moves with respect to frame S with constant velocity v in the positive x direction;
- coordinates of some event are
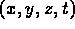 in frame S,
in frame S,
and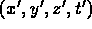 in frame S'
in frame S'
- relation between the two:

with
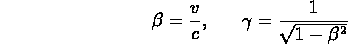
- note the symmetry between
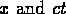 ;
;
- note that now the time is not the same in the two frames;
- both position and time are affected by the transformation, which can be represented as a ``rotation'' in a four-dimensional space in which ct is the coordinate of the fourth dimension;
- for
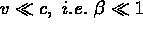 , the Lorentz transformation becomes the Galilei transformation.
, the Lorentz transformation becomes the Galilei transformation.
home page for phy1020
Tue Oct 15 15:12:41 EDT 1996